|
Anamorphic describes a method
used for squeezing 30-40% more wide screen resolution
onto a DVD movie. Wide screen DVD movies can present
more of the original theatrical format with a superior
image. Adjust the DVD player’s output to 16:9 for wide
screen for peak performance
Controls the sound level to
prevent wide variations in volume among different TV
Channels and types of programming.
Automatically tunes all
available channels in your area or cable system into
memory, and then lets you add or delete the channels of
your choice.
The
ability to listen to the audio from the main screen or
the picture-in-picture window, without moving the video
image around on the screen.
The
term "aspect ratio" describes the relationship between
the width and height of a TV screen. Traditional TVs
have an aspect ratio of 4:3, meaning that for every 4
inches of width, there are 3 inches of height. This
results in a screen that looks almost like a square.
Many newer TVs have an aspect ratio of 16:9, so their
screens are almost twice as wide as they are tall. Also
referred to as "wide screen," 16:9 TVs are better suited
to wide screen DVDs and HDTV broadcasts. The term
"aspect ratio" can also be used to describe the
dimensions in which film or TV shows are shot.
Traditional broadcasts are usually in 4:3 format, while
HDTV broadcasts have an aspect ratio of 16:9.
Automatically detects the
brightness levels of the input signal and adjusts the
backlight accordingly. It provides a maximum brightness
that's considerably greater than the level of
conventional systems, resulting in crisp, natural
pictures.
Dynamically adjusts the video
signal according to the image contrast. Working in
tandem with Active Light Control, it adds greater
brightness to bright scenes and brings more depth to
dark scenes, delivering more vivid images.
The
term "aspect ratio" describes the relationship between
the width and height of a TV screen. Traditional TVs
have an aspect ratio of 4:3, meaning that for every 4
inches of width, there are 3 inches of height. This
results in a screen that looks almost like a square.
Many newer TVs have an aspect ratio of 16:9, so their
screens are almost twice as wide as they are tall. Also
referred to as "wide screen," 16:9 TVs are better suited
to wide screen DVDs and HDTV broadcasts. The term
"aspect ratio" can also be used to describe the
dimensions in which a film or TV show are shot.
Traditional broadcasts are usually in 4:3 format, while
HDTV broadcasts have an aspect ratio of 16:9.
The
RAGE LT PRO is the first mobile accelerator to
incorporate an integrated Low Voltage Differential
Signaling (LVDS) I/O interface. ATI's advanced power
management system, a block-by-block power control,
results in lower power dissipation, helping to achieve
longer battery life. The RAGE LT PRO also offers
"Filtered Radiometric Expansion," which provides the
best quality image scaling possible, to fit any size LCD
panel. ATI's industry-leading TV-out technology,
ImpacTV2™, is integrated with the RAGE LT PRO chip to
support multi-screen viewing, and simultaneous outputs
to TV, CRT and LCD. The RAGE LT PRO chip also provides
the same high performance and functionality to the
emerging LCD flat panel monitor market.
| ATSC tuner is the main HDTV
Digital Receivers for HDTV TV. Regular tuner is
called NTSC tuner which receives the NTSC signals.
In a few years time, NTSC signals will be slowly
phased out in favor of HDTV signal. Therefore all
tuner will be change to ATSC tuner.
Right now, all Digital
TV requires separate NTSC & ASTC tuner to
receive both NTSC & HDTV signal
now.
|
Color gamut is the range of red,
green and blue the can be correctly rendered on a
display. NTSC standards set a range of colors that can
be transmitted. LCD panels that are able to display a
higher percentage of NTSC color gamut are superior for
watching television.
The
brightness of a display at full white over the
brightness of a display at full black. Because the black
value is greatly affected by ambient light, some TV
technologies calculate contrast ratio in darkened rooms.
LCD televisions are superior at rejecting ambient light
and maintaining contrast ratios in lit rooms.
Delivers outstanding
resolution and color accuracy of video images from a
variety of sources, including DVD players, by keeping
the Y, PR, PB of video images intact during the
transmission process.
Abbreviation of
Dual-scan STN, an enhanced STN passive
matrix LCD display. The screen is divided into halves,
and each half is scanned simultaneously, thereby
doubling the number of lines refreshed per second and
providing a sharper appearance. DSTN is widely used on
laptops.
|
Dual Page
Display |
|
1 |
|

Ultra Wide LCD
Screen are wide enough to allow Dual Page Display
of 2 programs on the screen simultaneously.
E.g user can have an Excel
spreadsheet display on the right side and Internet
Explorer display on the left side. However Dual
page display is NOT an automatic function on the
LCD monitor. User have to manually set the
position the dual page
view. |
Digital Versatile Disc – A
high-density compact disc for storing large amounts of
data, especially high-resolution audio-visual material.
Movies stored on DVD are higher resolution than those
stored on VHS videotape.
Digital Visual Interface – A
type of standard connector between the display and a
computer or other device. DVI is
Video only. DVI images are superior
to composite video and
S-Video signals.
DVI Port 
Used
by newer HDTV set-top boxes and DVD players, the
DVI-HDCP connection allows the transmission of
uncompressed, copy-protected digital content to your
high definition display with stunning image fidelity and
clarity.
This
technology utilizes the bottom substrate for both X and
Y-axis measurements. The flexible coversheet acts only
as a voltage-measuring probe. This means the touch
screen will continue working properly even with
non-uniformity in the coversheet's conductive coating.
The result is an accurate, durable and reliable touch
screen that offers drift-free operation. It is tested to
over 35 million finger touches with no performance
degradation (compare to 1 million touch life max. for
Four-Wire and Eight-Wire Technology). Moreover, this
advanced design allows flat, spherical (not available in
Four-Wire and Eight-Wire), and cylindrical designs.
Furthermore, Resistive Touch Screen Panel can be used
with any object to touch, e.g. finger, pen, pencil,
credit card, and many others. On the other hand,
Capacitive Touch Screen Panel only allows to use finger
to touch, which uses your body as a ground to measure
coordinates.
|
With Sceptre's feature,
"Flicker and Static Free", it is friendlier and
healthier for the users. Lots of people found
those two are annoying and unhealthy to use in an
extensive use. Screen Flicker results from a
variety of factors, the most important of which is
the monitor's refresh rate, the speed with which
the screen is redrawn. If the refresh rate is too
slow, the screen will appear to glimmer. Screen
Static is the noise produced in a radio or
television receiver by man-made electrical
disturbances.
Faroudja DCDi |
|
1 |
DCDi is a video mode algorithm that stands
for Directional Correlation
Deinterlacing. It was designed for video
based material like fast-paced sporting events. Its
purpose is to eliminate jagged edges (jaggies) along
diagonal lines caused by interpolation. If you remember,
you are not simply weaving together two fields of video
that match, you have to create new information through
the art of interpolation which is really a fancy way to
say you are guessing. DCDi monitors edge transitions and
fills in the gaps. The technology was introduced a few
years back in the digital format translator, a $50,000
system that broadcasters like CBS use to upconvert NTSC
to HD. It was/is used to upconvert standard definition
material (480i, what we have on conventional TV) to
enhanced definition quality (480p). You may already
being enjoying DCDi today on your digital TV.
In the Fig B below, you will see how
DCDi makes the lines much more dramatic, and it is
really a terrific illustration of how powerful DCDi is.
In Fig A, it is an enlarged area of the flag, with DCDi
turned off. You can see jagged lines. With DCDi turned
on (bottom, Fig B), the jagged lines are gone, and the
lines are smooth. This is a huge technical
accomplishment by Faroudja engineers.
Because DCDi is a video algorithm (an
algorithm is a series of mathematical formulas), you
might wonder how it affects viewing a film on TV.
Remember, in order to avoid artifacts, a video processor
will switch modes (film vs. video - video vs. film). If
the transition between video and film is not done
properly by the studio, it is called a Bad Edit. The
video processor will then treat the film material as
video during those sections of bad edits. There are a
couple of giveaways when the processor has switched from
film mode to video mode. First is the loss of
resolution. This is minimized because the Faroudja
algorithm is motion adaptive. The second is the
appearance of jaggies along diagonal edges. DCDi hides a
good portion of the jaggies, so you never realize when
it changes from and to film mode, which is the whole
point! DCDi makes the movie watching experience more
enjoyable because the annoying artifacts are all gone,
so all you have to worry about is whether there is any
more microwave popcorn in the kitchen
cabinet.

Bottom image is with DCDi
technology applied.
720p (Progressive),1080p &
1080i (Interlaced).
A
television set that is equipped to receive a digital
signal form an external high definition digital source,
like a cable box, satellite, or tuner.
HDMI
is a new standard digital connection between A/V
devices, such as a set-top box, DVD player or A/V
receiver, and a digital television. HDMI stands for High-Definition Multimedia
Interface, and like DVI, it allows for the
uncompressed data transfer of video between a digital TV
and HDMI-enabled consumer electronics devices.
According to the HDMI’s official Web site, the
advantages of HDMI are:
1) The highest quality video seen
and audio heard
2) Fewer cables behind the TV means
less mess and confusion-free connection
3)
Automatically configures remote controls of devices
connected by HDMI
4) Automatically adjusts video
content to most effective format
5) HDMI is
compatible with DVI, which means it will allow
connection to PCs
HDMI
Port

Sharpens the edges of objects
in the picture. Horizontal edge correction works in
conjunction with the dynamic sharpness control and
velocity modulated scan to help produce clean, crisp
television images and reduce the unwanted effects of
video noise. The vertical edge correction circuit works
in conjunction with the digital comb filter to sharpen
the horizontal edges of objects in the picture.
A
wide horizontal viewing angle lets viewers sit away from
the center seating position and still experience the
product.
Short for High-Performance
Addressing, a Passive-Matrix Display technology that
provides better response rates and contrast than
conventional LCD displays. Although HPA displays aren't
quite as crisp or fast as Active-Matrix (TFT) displays,
they're considerably less expensive to produce.
Consequently, HPA is being used by a number of computer
manufacturers for their entry level or value notebook
computers.
Abbreviation of Liquid
Crystal Display, a type of display used in digital
watches and many portable computers. LCD displays
utilize two sheets of polarizing material with a liquid
crystal solution between them. An electric current
passed through the liquid causes the crystals to align
so that light cannot pass through them. Each crystal,
therefore, is like a shutter, either allowing light to
pass through or blocking the light.
With
Sceptre's Light Weight and Slim Design features, it is
ideal to carry for the road trip, business presentation,
and many other purposes. This product has an easy
detachable base (no tool required³). This feature
reduces the unnecessary weight and space to carry for
the presentation. Most of all, it is to carry
around.
|
(PIP) Picture-in-picture
|
|
1 |
An
enhanced version of picture-in-picture offers a variety
of per-arrange formats that the user can choose from to
display more than one image on a screen. Some are
arrange to display simultaneous image from both a
computer and TV.
| QAM Tuner |
|
1 |
| QAM stands for "quadrature
amplitude modulation," the format by which digital
cable channels are encoded and transmitted via
cable. With the QAM tuner, users can
connect their cable directly to their TV and watch
any digital and/or HD cable station that is
not
encrypted. Integrated QAM tuner allows free
reception of unscrambled digital cable programming
offered by certain cable providers. Contact your
local provider for more information about the
availability of such content in your area.
|
| |
|
Resolution |
|
1 |
Refers to the sharpness and
clarity of an image. The term is most often used to
describe monitors, printers, and bit-mapped graphic
images. In the case of dot-matrix and laser printers,
the resolution indicates the number of dots per inch.
For example, a 300-dpi (dots per inch) printer is one
that is capable of printing 300 distinct dots in a line
1 inch long. This means it can print 90,000 dots per
square inch.
For
graphics monitors, the screen resolution
signifies the number of dots (pixels) on the entire
screen. For example, a 640-by-480 pixel screen is
capable of displaying 640 distinct dots on each of 480
lines, or about 300,000 pixels. This translates into
different dpi measurements depending on the size of the
screen. For example, a 15-inch VGA monitor (640x480)
displays about 50 dots per inch.
UXGA: A display
with 1200 x 1600 pixel resolution.
SXGA: A
display with 1280 x 1024 pixel
resolution.
XGA: A display with
1024 x 768 pixel resolution.
SVGA: A display
with 800 x 600 pixel
resolution.
VGA: A display with
640 x 480 pixel resolution.
Printers,
monitors, scanners, and other I/O devices are often
classified as high resolution, medium
resolution, or low resolution. The actual
resolution ranges for each of these grades is constantly
shifting as the technology improves.
Video RAM
Required for Different Resolutions
|
Resolution
|
256
colors
(8-bit) |
65,000
colors
(16-bit) |
16.7
million colors
(24-bit, true
color) |
|
640x480 |
512K |
1
MB |
1
MB |
|
800x600 |
512K |
1
MB |
2
MB |
|
1,024x768 |
1
MB |
2
MB |
4
MB |
|
1,152x1,024 |
2
MB |
2
MB |
4
MB |
|
1,280x1,024 |
2
MB |
4
MB |
4
MB |
|
1,600x1,200 |
2
MB |
4
MB |
6
MB |
Response time is a measure of
how long a display takes to change the image. A typical
LCD television is 2 to 3 times faster than the average
computer monitor LCD Fast response time is superior for
playing computer games and viewing action movies and
sports using TFT technology.
Abbreviation of Thin Film
Transistor, a type of LCD flat-panel display screen,
in which each pixel is controlled by from one to four
transistors. The TFT technology provides the best
resolution of all the flat-panel techniques, but it is
also the most expensive. TFT screens are sometimes
called Active-Matrix LCDs.
This
input is used on most electronic devices, allow a signal
line and sound signal connection.
MVA Technology allows wider viewing angle from the
both sides of LCD.
In more technical terms, the
conventional multi-domain vertical alignment (MVA)
technology has smaller viewing angle in the azimuth
angle of 45 degree.
The viewing angle of MVA LCD is
increased to 80 degree in all azimuth angle by CMO'
Super MVA technology
This
input is used for video cameras, VCR’s, DVD players,
game stations.
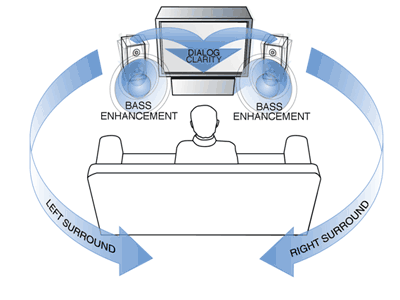
SRS TruSurround XT is the
second generation of SRS TruSurround. Building upon its
patented predecessor, TruSurround XT solves the problem
of playing 5.1 or 6.1 multichannel content over two
speakers (or headphones). TruSurround XT accepts
input from up to a seven channel (6.1) audio source and
processing a two-channel output. When receiving
multichannel content, TruSurround XT virtualizes the
channels, creating "phantom" speakers that appear to
extend all around the listener. When receiving mono or
stereo content, TruSurround XT presents an expansive
three dimensional sound field. It makes the sound richer
and real.
Component Video input used
for wide screen formats on most DVD players and HDTV
viewing.
Short for Extended
Graphics Array, a high-resolution graphics standard
introduced by IBM in 1990. XGA was designed to replace
the older 8514/A video standard. It provides the same
resolutions (640 by 480 or 1024 by 768 pixels), but
supports more simultaneous color (65 thousand compared
to 8514/A's 256 colors). In addition, XGA allows
monitors to be
non-interlaced. | 




